- News
- lifestyle
- health-fitness
- fitness
- Why vitamin D needs this mineral to support our liver and kidneys
Trending
Why vitamin D needs this mineral to support our liver and kidneys
Vitamin D needs this mineral to work effectively, as it activates vitamin D, helping the body to use it properly. If you’re taking vitamin D for better health, don’t forget about it! Without it, vitamin D cannot work effectively, leaving your liver and kidneys at risk. By ensuring you have enough of this mineral, you allow your body to fully absorb and utilize vitamin D, leading to stronger bones, improved immunity, and better organ function.
Vitamin D is known as the sunshine vitamin, essential for bone health, immunity, and overall well-being. But did you know that without magnesium, vitamin D may not work effectively? Magnesium is a much-needed mineral that activates vitamin D and helps the body use it properly. If you’re taking vitamin D supplements but not getting enough magnesium, your liver and kidneys may not fully benefit. Here is everything we need to know about why magnesium is essential and how it supports these vital organs.
Magnesium might just be the key to unlocking vitamin D
Many people focus on getting enough vitamin D, either from sunlight, food, or supplements. However, without magnesium, vitamin D remains inactive in the body. Magnesium is needed to convert vitamin D into its usable form, called . Without this conversion, vitamin D cannot perform its functions, including regulating calcium and phosphorus levels, which are critical for kidney and liver health.

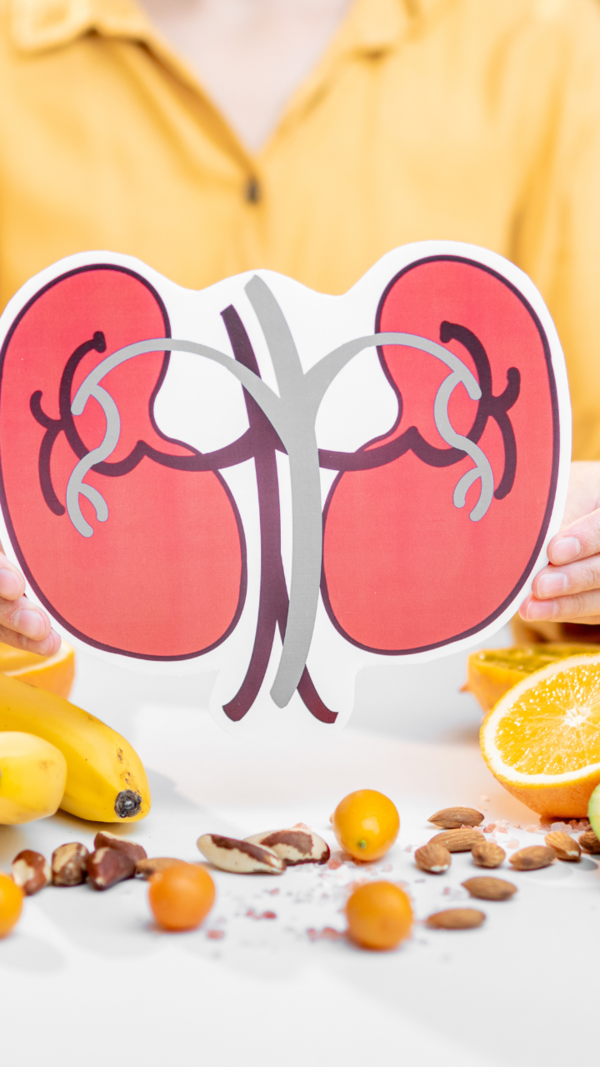
How magnesium supports kidney health
Our kidneys have a role in processing vitamin D. They help convert it into its active form, which allows our body to absorb calcium efficiently. When magnesium levels are low, this process slows down, leading to vitamin D deficiency symptoms even if you’re getting enough of it.
Magnesium prevents kidney damage by reducing the . Since vitamin D increases calcium absorption, too much calcium without enough magnesium can lead to deposits in the kidneys, forming painful stones. Maintaining the right magnesium levels ensures that calcium is used properly rather than accumulating in unwanted places.

<p>Magnesium is essential for muscle function, nerve transmission, and energy production. <br></p>
Role of magnesium in liver function
The liver is another key organ involved in processing vitamin D. Before the kidneys activate it, vitamin D first goes through the liver, where it is converted into a form that the kidneys can use. If magnesium is insufficient, this liver function becomes inefficient, leading to poor vitamin D metabolism.
Magnesium also helps detoxify the liver and reducing inflammation. suggest that a magnesium-rich diet may lower the risk of fatty liver disease, a condition that affects many people due to poor dietary habits and lifestyle choices.
Signs one might be deficient in magnesium
Magnesium deficiency is common, yet many people don’t realize it. Some symptoms include:
- Muscle cramps and spasms
- Fatigue and weakness
- Irritability and mood swings
- Sleep disturbances
- Frequent headaches
- High blood pressure
If you experience any of these symptoms, it might be time to check your magnesium intake.
How to get enough magnesium
The good news is that magnesium is widely available in many foods. To boost your levels naturally, include these magnesium-rich foods in your diet:
- Leafy greens (spinach)
- Nuts and seeds (almonds, cashews, pumpkin seeds)
- Whole grains (brown rice, quinoa, oats)
- Legumes (lentils, chickpeas, black beans)
- Dark chocolate (in moderation!)
- Bananas and avocados
If you struggle to get enough magnesium from food, magnesium supplements can also help, but it’s always best to consult a doctor before taking them.

About the Author
TOI Lifestyle DeskEnd of Article
FOLLOW US ON SOCIAL MEDIA
Visual Stories
Tired of too many ads?